Compact De-NOx SCR System with In-house De-NOx Catalyst
- Main Applications
Industrial incinerators, Waste incinerators, Boiler, Power generators
- Applications
- Functions
Basic Information
Nippon Shokubai’s De-NOx system utilizes Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology to remove nitrogen oxides (NOx) from flue gas emitted by power plant boilers, gas turbines, and various other combustion sources. A reducing agent, such as ammonia or urea, is injected into the exhaust steam upstream of a honeycomb-structured catalytic reactor, where NOx is converted into harmless nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O).
Nippon Shokubai’s advanced De-NOx system delivers exceptional, long-lasting NOx removal performance with minimal ammonia slip and low pressure drop.
De-NOx System Diagram
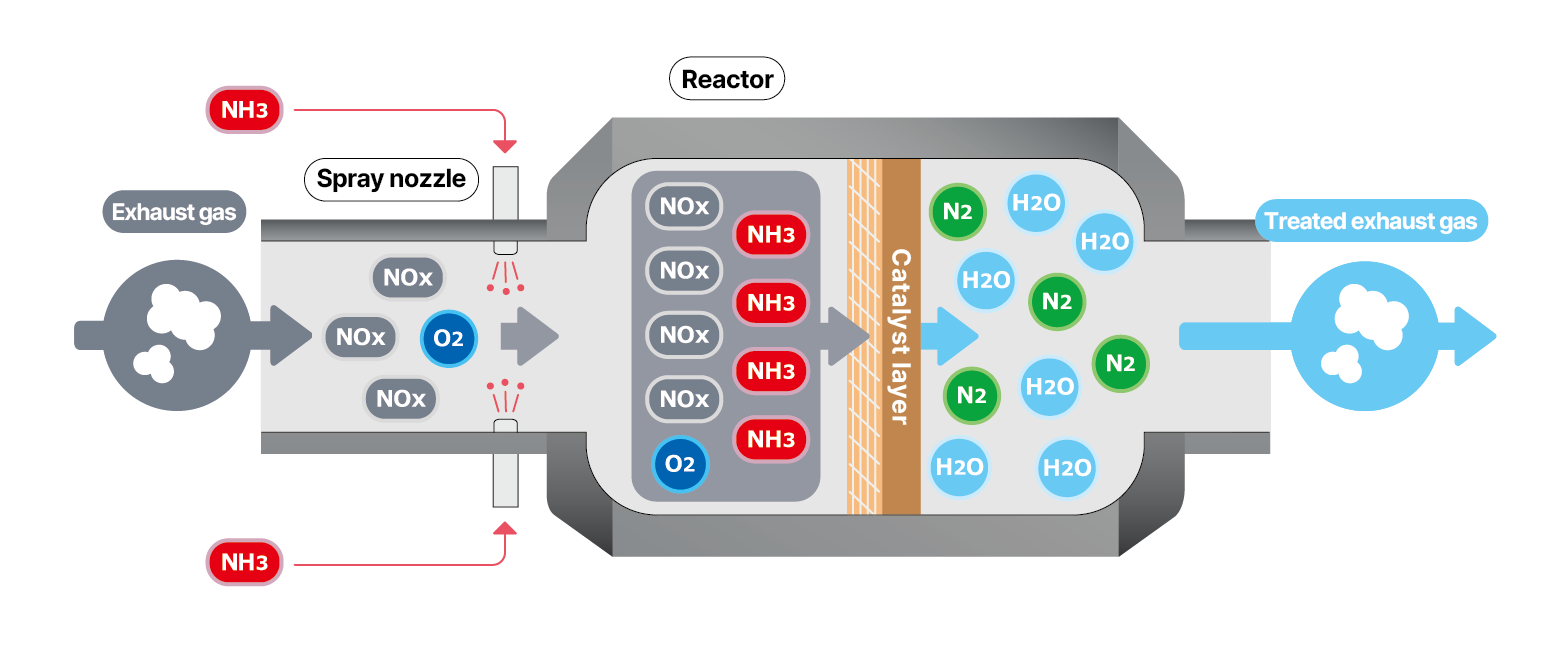
Features and Properties
- Nippon Shokubai began its De-NOx system business in 1987. Since then, we have built an extensive track record of deliveries for a wide range of applications, including industrial and waste incinerators, boilers, and various types of power generators.
- Our engineering team designs and manufactures tailor-made De-NOx systems using proprietary catalysts uniquely developed by Nippon Shokubai to meet the specific needs of each customer.
- Our compact De-NOx systems are engineered to fit within each customer’s available installation space, effectively handling high concentration of NOx and challenging exhaust gas conditions that require high NOx removal efficiency.
Installation Example
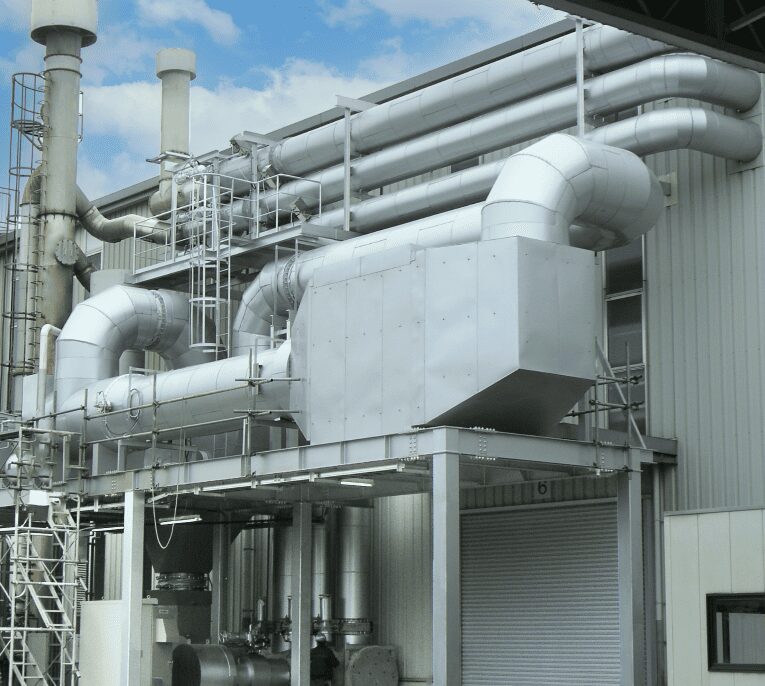
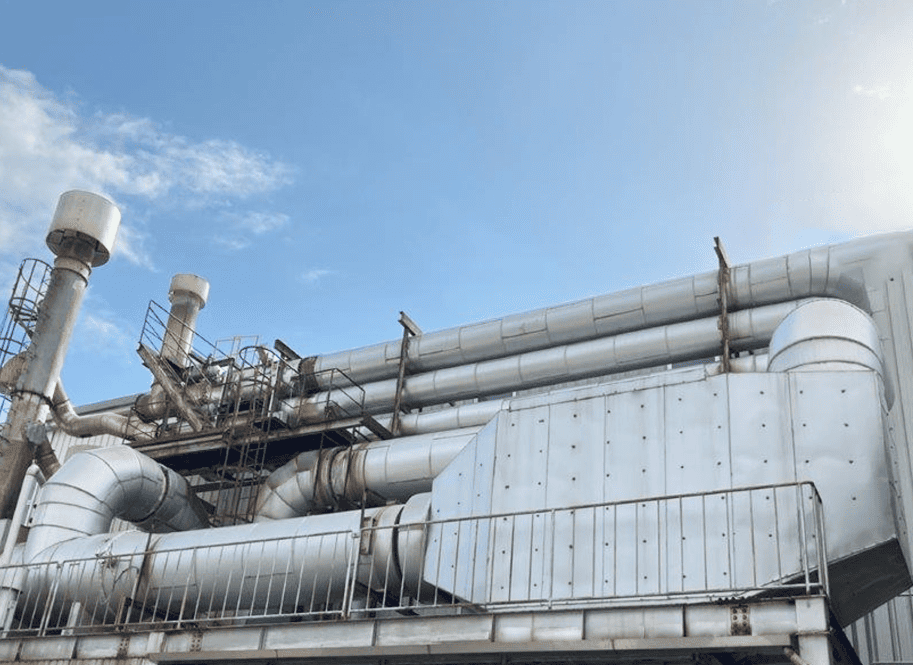


- Application : Industrial Furnace
- Exhaust Gas Treatment Capacity : Approx.24,800m3N/h
- Operation Started : 2006
(Photos : Left-During Installation in 2006 Right-19 Years After the Start of Operation)
System Overview
- A precise amount of reducing agent, equivalent to the quantity of NOx to be removed, is sprayed into the exhaust gas through a specially designed injection nozzle. The injection volume is automatically adjusted according to load fluctuations.
- The exhaust gas, with the reducing agent evenly dispersed, then passes through a catalyst layer in the reactor, where the NOx is decomposed into harmless nitrogen and water.
System Flow Diagram -1
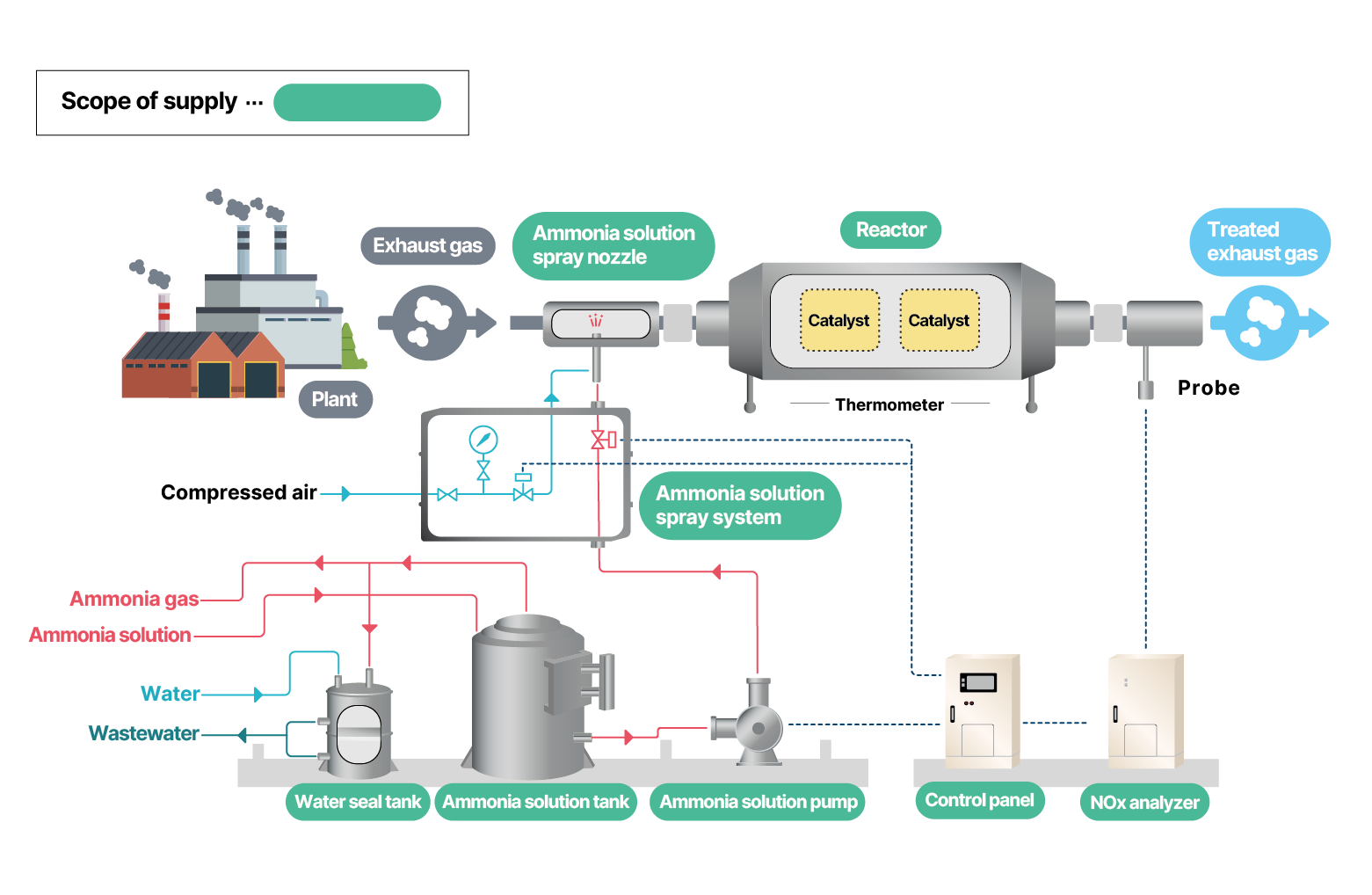
System Flow Diagram -2
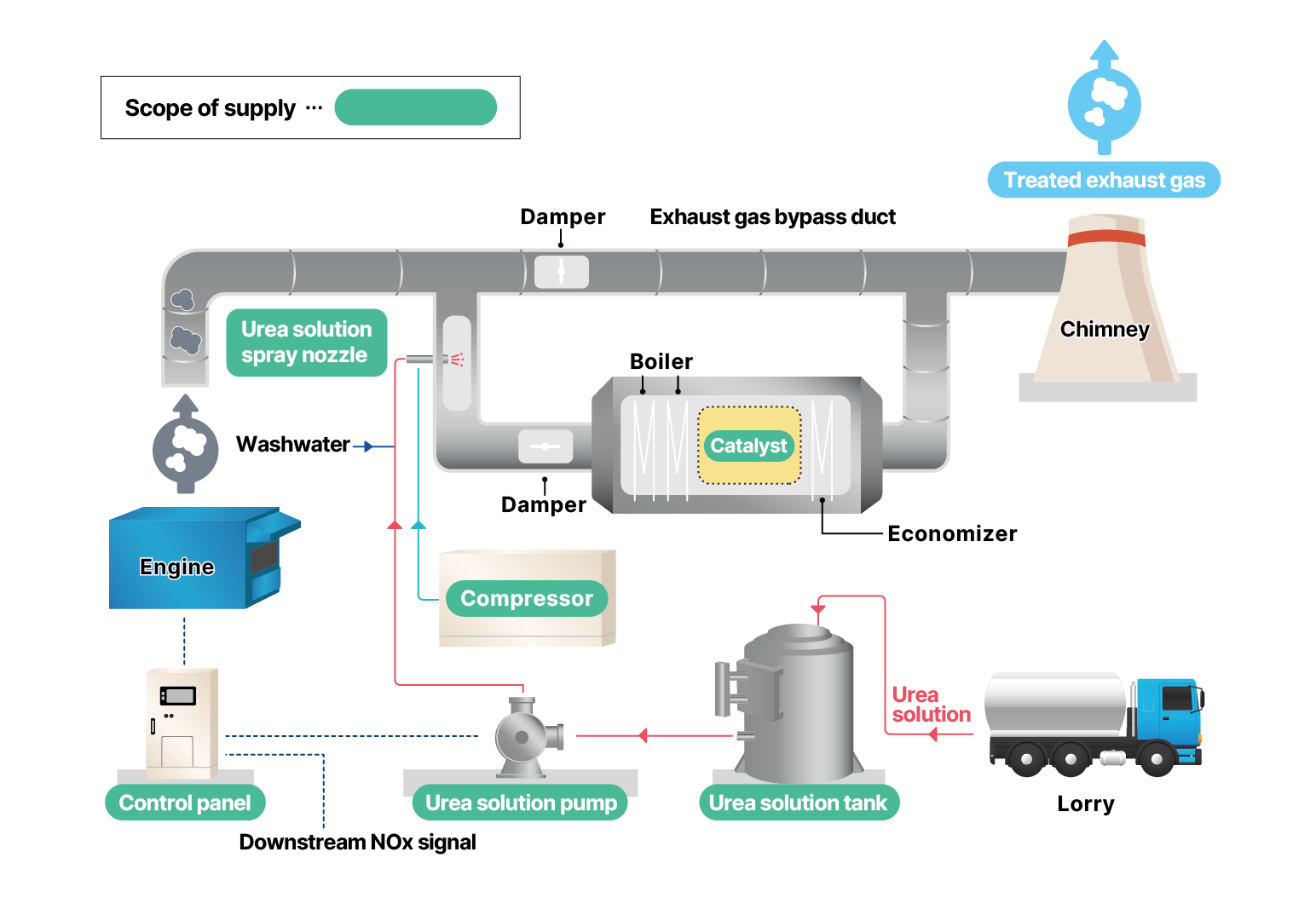
Examples of Applications
Examples of Use
| Industrial incinerators | Waste incinerators | Power generators | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas turbines | Diesel engines | Gas engines | ||||
| Exhaust Gas Composition | Gas Volume (Nm3/h) | 2,000 – 55,000 | 10,000 – 75,000 | 15,000 – 80,000 | 3,000 – 45,000 | 10,000 – 40,000 |
| NOx (ppm) | 10 – 2,500 | 100 – 500 | 30 – 150 | 800 – 1,500 | 50 – 250 | |
| O2 (%) | 5 – 21 | 5 – 12 | 12 – 18 | 10 – 13 | 10 – 15 | |
| SOx (ppm) | 0 – 30 | 1 – 30 | 0 – 1 | 0 – 200 | 0 – 5 | |
| H2O (%) | 1 – 25 | 15 – 35 | 4 – 7 | 4 – 7 | 8 – 12 | |
| Catalyst Performance | Processing Temperature (°C) | 175 – 300 | 175 – 220 | 200 – 380 | 330 – 400 | 350 – 400 |
| SV (h-1) | 1,000 – 8,000 | 1,500 – 4,000 | 8,000 – 20,000 | 5,000 – 15,000 | 5,000 – 15,000 | |
| NOx Removal Efficiency (%) | 60 – 98 | 50 – 95 | 70 – 90 | 20 – 92 | 80 – 95 | |
We can propose a De-NOx system to suit your project requirements. Please feel free to contact us for more information.