Hybrid Monomers VEEA™, VEEM™ Dual-functional monomer with acrylate and vinyl ether reactivity
- Main Applications
Ink, Coating, Photo resist, Adhesives, Stereo lithography
- Applications
- Functions
Basic Information
VEEA™: 2- (2-Vinyloxyethoxy)ethyl acrylate
VEEM™: 2- (2-Vinyloxyethoxy)ethyl methacrylate (under developing)
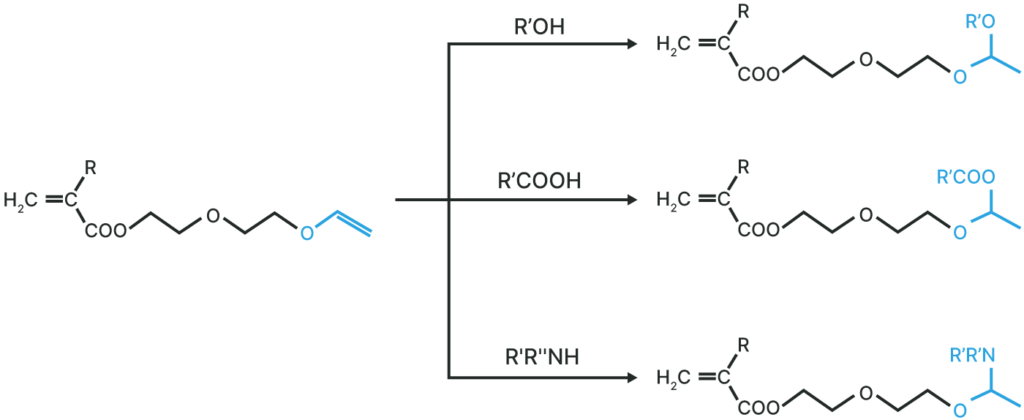
This monomer has a unique structure that contains both a radically polymerizable reactive group and a cationically polymerizable reactive group within a single molecule.
By selecting the polymerization method, a unique polymer with either an acryloyl group or a vinyl ether group on the pendant can be obtained.
VEEA™ and VEEM™ have excellent UV curability as monomers.
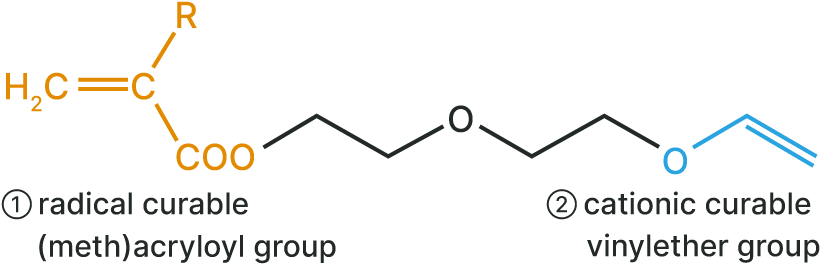
(1) Radical polymerizable (meth)acryloyl group
- Polymerization is not inhibited by water and bases
- Has many co-polymerizable monomers
- Has no dark reaction
(2) Cationic polymerizable vinyl ether group
- Polymerization is not inhibited by oxygen
- Good dilutability
- Good adhesion
| VEEA™ | VEEM™ | |
|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 86273-46-3 | 76392-22-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H14O4 | C10H16O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 186.20 | 200.23 |
| Appearance | Colorless and transparent liquid | Colorless and transparent liquid |
| Boiling Point | 115 – 116°C/13.3 hPa | 122 – 123°C/13.3 hPa |
| Specific Gravity | 1.04g/mL(15℃) | 1.03 g/mL (15°C) |
| Viscosity | 3.65 mPa·s | 3.19 mPa·s |
| Solubility | H2O:18g/L(30℃) Organic solvent: Dissolve arbitrarily | H2O:2.2g/L(30℃) Organic solvent: Dissolve arbitrarily |
Features and Properties
Features and Properties as Monomers
- Low viscosity
- Low odor, low skin irritation, and low toxicity
- Fast curing under UV and EB irradiation
- Less sensitive to oxygen inhibition during polymerization
Features and Properties of Cured Material
- Excellent adhesion to various substrates
- Flexibility and scratch resistance
- High solvent resistance
Polymerization Method
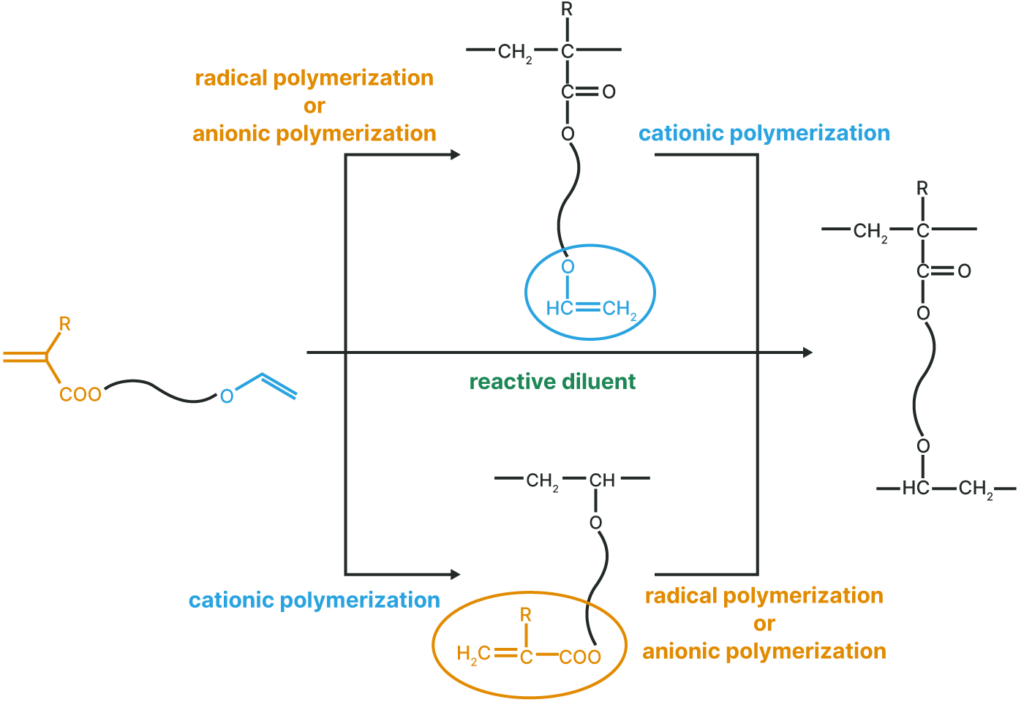
Details of Functions
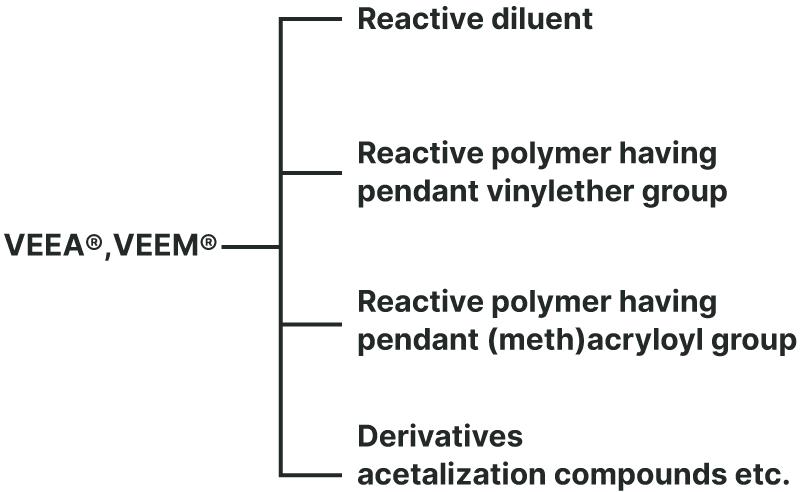
Reactive Diluent
- VEEA™ and VEEM™ can be used as a reactive diluent for heat, UV and EB curable inks.
- VEEA™ and VEEM™ are less sensitive to curing inhibition by oxygen in the air, and can cure even in thin coating films (a few microns)

UV Curing Properties of VEEA™
| Run No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEEA™ | 100 | – | – | |
| DEGDA | – | 100 | 53.53 | |
| DEGDV | – | – | 46.47 | |
| Irgacure907 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| UV curing performance (1) | 0.1 J/cm2 | – | – | — |
| 0.2 J/cm2 | – | – | — | |
| 0.3 J/cm2 | ++ | + | — | |
| 0.4 J/cm2 | ++ | + | — | |
| 0.5 J/cm2 | ++ | + | — | |
| UV curing performance (2) | 1 pass | ++ | – | — |
| 2 pass | ++ | – | — | |
| 3 pass | ++ | – | — | |
| 4 pass | ++ | – | — | |
| 5 pass | ++ | – | — | |
UV curing performance (1): UV irradiation equipment: PM25C-100 (USHIO Inc.) 250 W ultra-high pressure mercury vapor lamp (main wavelength = 365 nm), thickness: 300 μm, surface tackiness: judged by finger touch (++ = tack-free, — = uncured) (++ = tack-free, — = not cured)
UV curing performance (2): UV irradiation device: UB031-5BM (EyEGRAPHICS), 80 W high pressure mercury vapor lamp, thickness: 30 μm, line speed: 14 m/min, distance from light source: 10 cm, irradiation energy per pass: 125 mJ/cm2, Irradiation energy per pass: 125 mJ/cm2, Surface tackiness: Tack-free to the touch (++ = tack-free, — = not cured)
UV Curing Properties of VEEA™ and VEEM™ as Reactive Diluents
| Run No. | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unsaturated polyester resins | 60 | 60 | 60 | – | – | – | |
| Bis A type epoxy resin | – | – | – | 60 | 60 | 60 | |
| VEEA™ | 40 | – | – | 40 | – | – | |
| VEEM™ | – | 40 | – | – | 40 | – | |
| DEGDA | – | – | 40 | – | – | 40 | |
| Irgacure907 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Viscosity (mPa・s @ 25℃) | 1102 | 1038 | 2670 | 295 | 289 | 855 | |
| UV curing performance | 1 pass | + | – | – | – | – | – |
| 2 pass | + | – | – | ++ | – | ++ | |
| 3 pass | ++ | – | – | ++ | – | ++ | |
| 4 pass | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | ++ | |
| 5 pass | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| 7 pass | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| Pencil Hardness (JIS K-5400) | F | HB | B | F | F | F | |
| Acetone rubbing (100times) | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
UV curing performance: UV irradiation device: UB031-5BM (EYEGRAPHICS Co., Ltd.) with 80 W high-pressure mercury lamp;
Thickness: 30 μm, Line speed: 14 m/min, Distance from light source: 10 cm, Irradiation energy per pass: 125 mJ/cm2, Surface tackiness: determined by finger touch (++ = tack free, — = uncured) Pencil hardness: measured after 10 passes curing. Acetone rubbing: measured after 10 passes curing
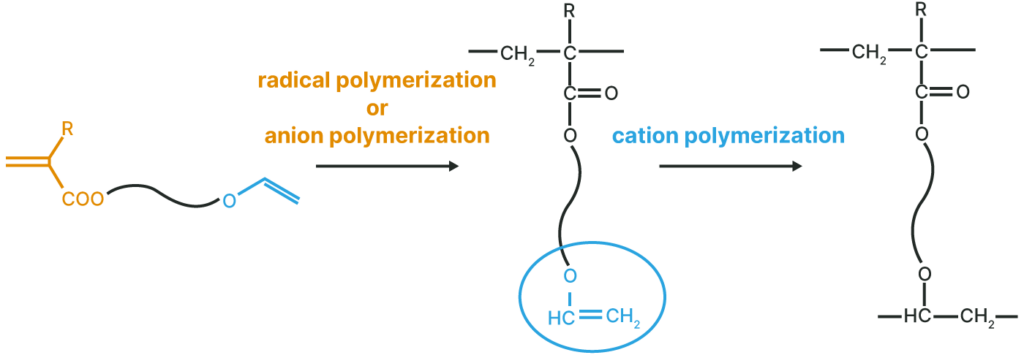
Polymer with a Pendant Vinyl Ether Group
Thermal, UV, and EB curable polymers are obtained by radical or anionic polymerization.
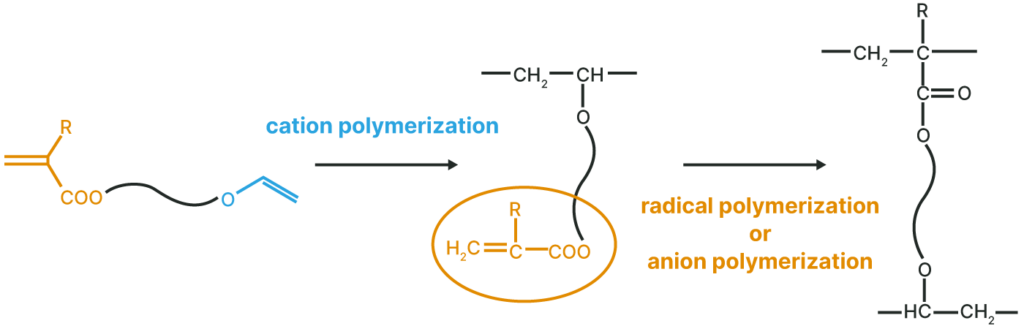
Polymer with a Pendant (Meth)Acryloyl Group
Thermal, UV, and EB curable polymers are obtained by cation polymerization.
Derivatives
Various acetals can be synthesized by addition reaction to vinyl ether groups.
Examples of Uses
Examples of Applications
- Coatings: Wood coatings, Film coatings, Hard coatings, Optical disk coatings, Optical fiber coatings, etc.
- Ink: Inkjet inks, Screen inks, Offset inks, Gravure inks, etc.
- Photo Resists: Dry film resist, Semiconductor resist, Photosensitive resin plate, etc.
- Adhesives
- Stereo-lithography
etc.