Hybrid Monomers VEEA™, VEEM™ Hybrid monomers
- Main Applications
Ink, Coating, Photo resist, Adhesives, Stereo lithography
- Applications
- Functions
Basic Information
VEEA™: 2- (2-Vinyloxyethoxy)ethyl acrylate
VEEM™: 2- (2-Vinyloxyethoxy)ethyl methacrylate (under developing)
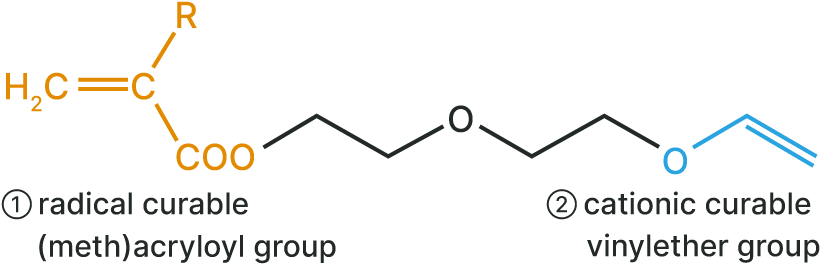
(1) Radical polymerizable (meth)acryloyl group
- Polymerization is not inhibited by water and bases
- Has many co-polymerizable monomers
- Has no dark reaction
(2) Cationic polymerizable vinyl ether group
- Polymerization is not inhibited by oxygen
- Good dilutability
- Good adhesion
| VEEA™ | VEEM™ | |
|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 86273-46-3 | 76392-22-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H14O4 | C10H16O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 186.20 | 200.23 |
| Appearance | Colorless and transparent liquid | Colorless and transparent liquid |
| Boiling Point | 115 – 116°C/13.3 hPa | 122 – 123°C/13.3 hPa |
| Specific Gravity | 1.04g/mL(15℃) | 1.03 g/mL (15°C) |
| Viscosity | 3.65 mPa·s | 3.19 mPa·s |
| Solubility | H2O:18g/L(30℃) Organic solvent: Dissolve arbitrarily | H2O:2.2g/L(30℃) Organic solvent: Dissolve arbitrarily |
Features and Properties
- VEEA™ and VEEM™ are monomers with unique structures having different types of polymerizable functional groups in one molecule: radical polymerizable (meth)acryloyl groups and cationic polymerizable vinyl ether groups.
- By selecting the polymerization method, unique polymers with (meth)acryloyl or vinyl ether groups as pendant groups can be obtained.
- VEEA™ and VEEM™ have excellent UV curability as monomers.
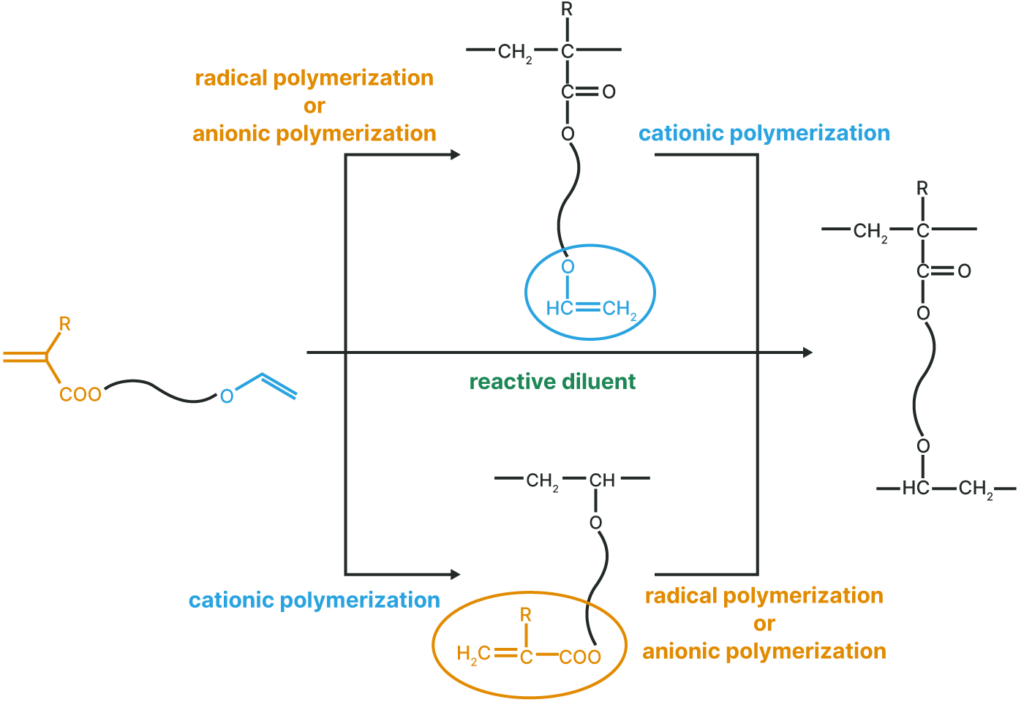
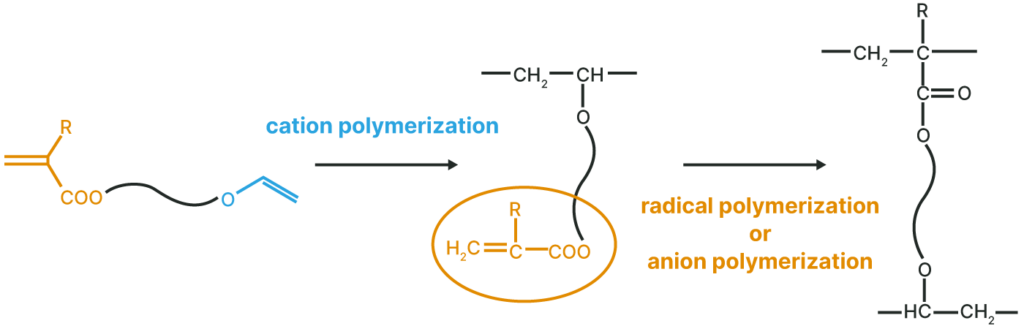
Polymerization Method
Details of Functions
Reactive diluent
- VEEA™ and VEEM™ can be used as a reactive diluent for heat, UV and EB curable inks.
- VEEA™ and VEEM™ are less sensitive to curing inhibition by oxygen in the air, and even thin films (several microns)

UV Curing Properties of VEEA™
| Run No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEEA™ | 100 | – | – | |
| DEGDA | – | 100 | 53.53 | |
| DEGDV | – | – | 46.47 | |
| Irgacure907 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| UV curing performance (1) | 0.1 J/cm2 | – | – | — |
| 0.2 J/cm2 | – | – | — | |
| 0.3 J/cm2 | ++ | + | — | |
| 0.4 J/cm2 | ++ | + | — | |
| 0.5 J/cm2 | ++ | + | — | |
| UV curing performance (2) | 1 pass | ++ | – | — |
| 2 pass | ++ | – | — | |
| 3 pass | ++ | – | — | |
| 4 pass | ++ | – | — | |
| 5 pass | ++ | – | — | |
UV curing performance (1): UV irradiation equipment: PM25C-100 (USHIO Inc.) 250 W ultra-high pressure mercury vapor lamp (main wavelength = 365 nm), thickness: 300 μm, surface tackiness: judged by finger touch (++ = tack-free, — = uncured) (++ = tack-free, — = not cured)
UV curing performance (2): UV irradiation device: UB031-5BM (EyEGRAPHICS), 80 W high pressure mercury vapor lamp, thickness: 30 μm, line speed: 14 m/min, distance from light source: 10 cm, irradiation energy per pass: 125 mJ/cm2, Irradiation energy per pass: 125 mJ/cm2, Surface tackiness: Tack-free to the touch (++ = tack-free, — = not cured)
UV curing properties of VEEA™ and VEEM™ as reactive diluents
| Run No. | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unsaturated polyester resins | 60 | 60 | 60 | – | – | – | |
| Bis A type epoxy resin | – | – | – | 60 | 60 | 60 | |
| VEEA™ | 40 | – | – | 40 | – | – | |
| VEEM™ | – | 40 | – | – | 40 | – | |
| DEGDA | – | – | 40 | – | – | 40 | |
| Irgacure907 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Viscosity (mPa・s @ 25℃) | 1102 | 1038 | 2670 | 295 | 289 | 855 | |
| UV curing performance | 1 pass | + | – | – | – | – | – |
| 2 pass | + | – | – | ++ | – | ++ | |
| 3 pass | ++ | – | – | ++ | – | ++ | |
| 4 pass | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | ++ | |
| 5 pass | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| 7 pass | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| Pencil Hardness (JIS K-5400) | F | HB | B | F | F | F | |
| Acetone rubbing (100times) | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
UV curing performance: UV irradiation device: UB031-5BM (EYEGRAPHICS Co., Ltd.) with 80 W high-pressure mercury lamp;
Thickness: 30 μm, Line speed: 14 m/min, Distance from light source: 10 cm, Irradiation energy per pass: 125 mJ/cm2, Surface tackiness: determined by finger touch (++ = tack free, — = uncured) Pencil hardness: measured after 10 passes curing. Acetone rubbing: measured after 10 passes curing
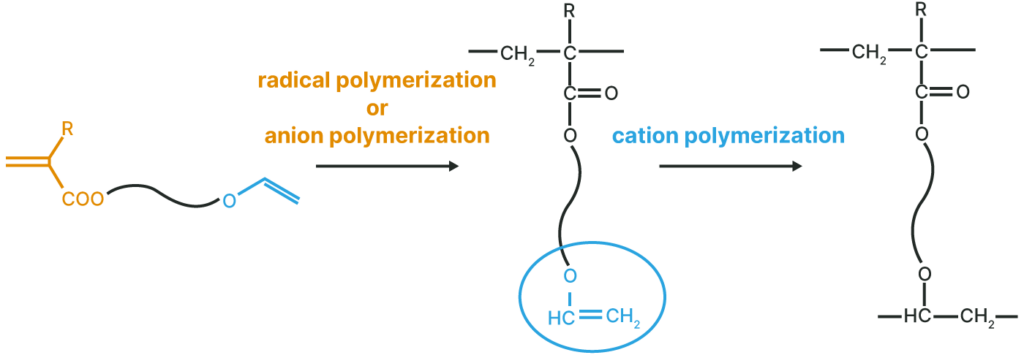
Polymer with a pendant Vinyl Ether Group
Thermal, UV, and EB curable polymers are obtained by radical or anionic polymerization.
Polymer with a pendant (Meth)Acryloyl Group
Thermal, UV, and EB curable polymers are obtained by cation polymerization.
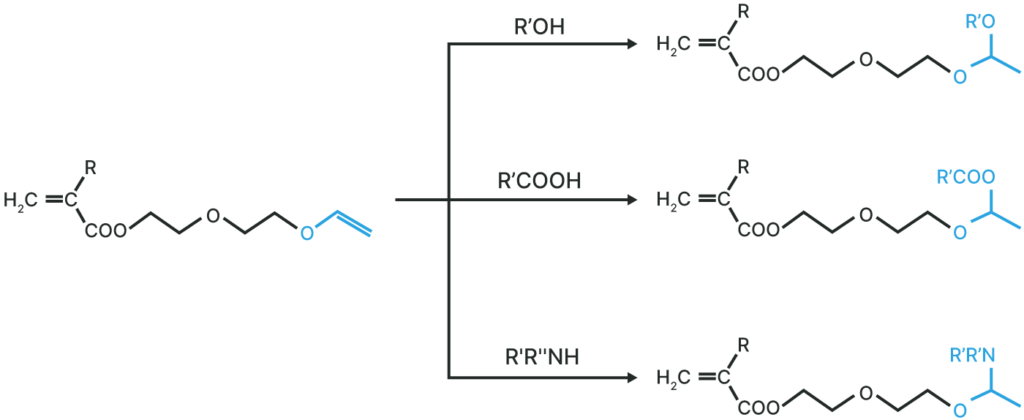
Derivatives
Various acetals can be synthesized by addition reaction to vinyl ether groups.
Examples of Applications
- Coatings: Wood coatings, Film coatings, Hard coatings, Optical disk coatings, Optical fiber coatings, etc.
- Ink: Inkjet inks, Screen inks, Offset inks, Gravure inks, etc.
- Photo Resists: Dry film resist, Semiconductor resist, Photosensitive resin plate, etc.
- Adhesives
- Stereo-lithography
etc.
Utilities