Cyclopolymerization Monomer: AOMA™ Specialty Acrylate monomer
- Applications
- Functions
Basic Information
AOMA™ combines hardness and toughness and improves adhesion to a variety of substrates!
Low viscosity and highly reactive cyclopolymerizable monomer
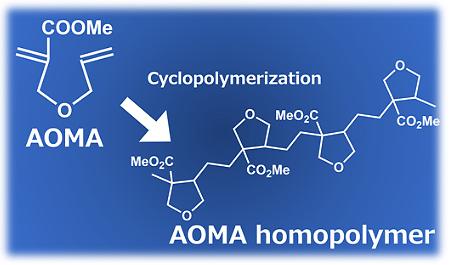
AOMA™ is a new cyclopolymerization monomer developed by Nippon Shokubai.
Polymers with a ring structure in the main chain can be obtained by radical polymerization.
| Chemical Formula | C8H12O3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 156.18 |
| Boiling Point | 84°C (2 kPa) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.01 g/cm³ (20°C) |
| Viscosity | 1.57 mPa·s (25°C) |
| Solubility | Soluble in various organic solvents, slightly soluble in water |
Features and Properties
Monomer: low viscosity, excellent dilutability and rapid UV curability
Polymer: Good adhesion to various substratesCombination of “hardness and heat resistance” and “flexibility and toughness”
Examples of Applications
AOMA™ has one of the lowest viscosities among existing functional monomers. AOMA™ has excellent dissolution and dilution properties for various oligomers and polymers, and exhibits high radical polymerization properties similar to those of acrylic monomers. When used as a reactive diluent, the main agent can be blended at high concentrations, and its inks can perform better than conventional products in applications such as UV-curable inkjet inks.

AOMA™ polymers are highly evaluated as a material that combines “hardness and heat resistance” and “flexibility and restorative properties,” both of which were conventionally considered difficult to achieve. AOMA™ is effective in achieving resilience and heat resistance for items printed by UV curable 3D printers. AOMA™ exhibits good adhesion to a wide range of substrates, including glass, metals, and various plastics, and is expected to be applied to a variety of applications, including coatings for flexible devices and adhesives for binding different substrates.

