Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)
- Main Applications
Batteries, Films for water treatment and dialysis, Adhesives, Ceramics, Ink, Printing, Fibers and textiles, Personal care products, Semiconductors
- Applications
- Functions
Basic Information
| Chemical Structure | 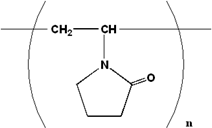 |
|---|---|
| CAS No. | 9003-39-8 |
| Chemical Substances Control Act (CSCA) No. | (6)-1048 |
| Industrial Safety and Health Act No. | CSCA No. is applied with necessary modifications |
Product Details
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is a nonionic, water-soluble polymer with the following features. It can be suitable for the usage of various applications and fields.
- Soluble in various solvents (e.g.: water, alcohol, amide and chlorineated solvents)
- Heat Resistance (Tg=160-170℃)
- Highly hygroscopicity
- Good film-forming properties
- Adhesion
- Ability to form complexes
Product Grades (Typical properties)
| Product Number | K-30 | K-85 | K-90 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | White powder | White powder | White powder |
| K-value※1 | 27.0 – 33.0 | 83.0 – 87.0 | 88.0 – 96.0 |
| Solid Content (wt%) | ≥ 95.0 | ≥ 95.0 | ≥ 95.0 |
| Water Content (wt%) | < 5.0 | < 5.0 | < 5.0 |
| Residual Monomers (NVP) (ppm) | < 100 | < 100 | < 100 |
| pH※2 | 3.0 – 7.0 | 5.0 – 9.0 | 5.0 – 9.0 |
※1:Fikentscher’s value of viscosity characteristics K-value represents a viscosity index relating to molecular weight and is calculated by the following Fikentscher’s formula with relative viscosity which is measured by capillary viscometer at 25 C
K=(1.5 logηrel -1)/(0.15+0.003c)+(300clogηrel+(c+1.5clogηrel )2)1/2/(0.15c+0.003c2)
ηrel:Relative viscosity of a PVP aqueous solution to water
c: Concentration (%) of PVP in an aqueous PVP solution
*2: Value of 10% aqueous solution
Examples of Applications
| Fields | PVP Features | |
|---|---|---|
| Batteries | Dispersants | Dispersion of metal oxides and carbon materials
Soluble in water and NMP to make slurry |
| Membranes for water treatment and dialysis | Compatibilizers
Hydrophilic agents Pore forming agents | Soluble in amide solvents, and disperses uniformly in polysulfones, etc.
Highly hydrophilic, Forms pores by washing membranes in water, Makes hydrophobic film surfaces hydrophilic |
| Adhesives | Pressure-sensitive adhesives
Rewetting adhesives Food packaging (non-contact) | Adhesion to a wide range of base materials such as plastics, glass, and metals etc. Highly hydrophilic, highly water-absorbing Low toxicity |
| Ceramics | Binders
Dispersants | Excellent dispersion of metal oxides
Binds to a wide range of materials |
| Ink, Printing, Fibers and textiles | Dispersants
Sizing agents | Pigment dispersion, binding properties
Easily water soluble |
| Personal care products | Setting agents
Thickeners Humectants | Highly adhesive, easily water soluble
Form retention Hydrophilic |
| Semiconductors | Resist
Polishing solutions Cleaning solutions | Easily water soluble, dispersion of inorganic substances |
Details of Functions
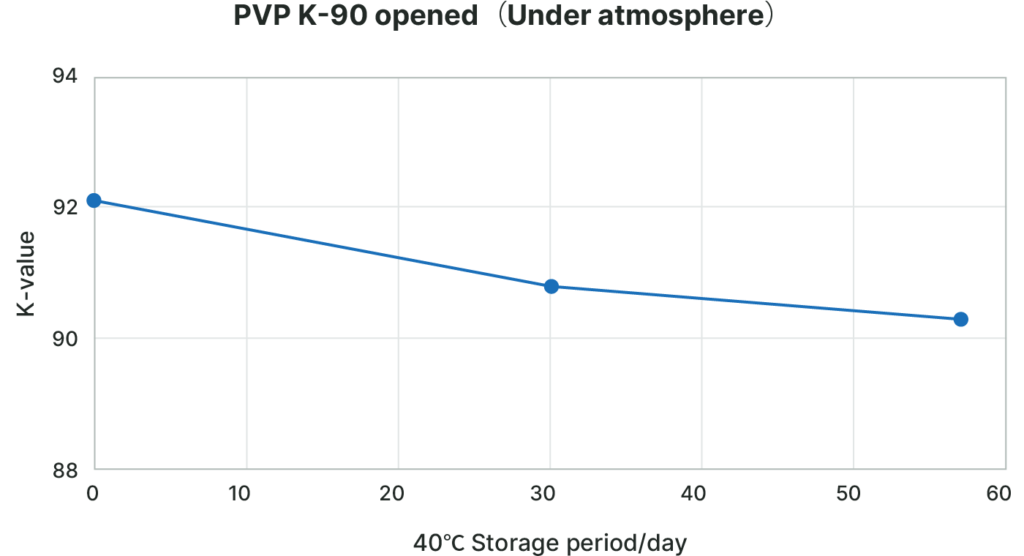
Excellent storage stability
This product has excellent storage stability, less decrease in K Value in the presence of the air.
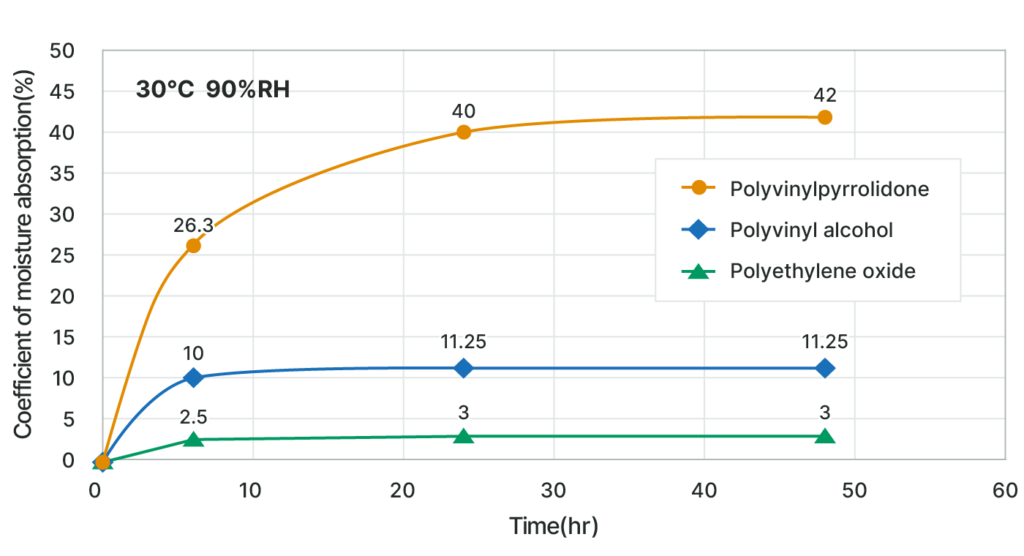
Superior hygroscopicity
This product has superior hygroscopicity compared to other nonionic, water-soluble polymers.
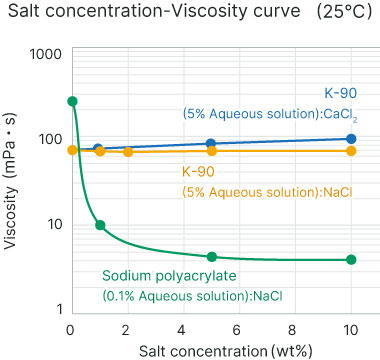
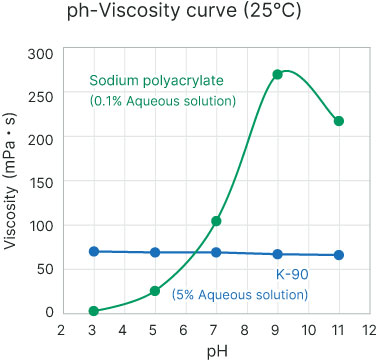
Excellent viscosity stability
With this product, it is possible to achieve an aqueous solution with stable viscosity, even with changes in the salt concentration or pH.
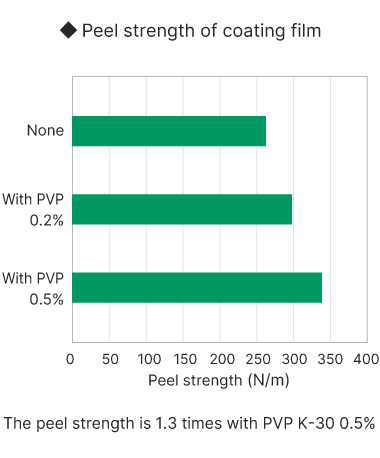
Superior adhesion
This product has superior adhesion to various base materials.
| Base Materials | Evaluation |
|---|---|
| PET films | ○ (non-peel off) |
| Nylon films | ○ |
| Flexible PVC films | ○ |
| PP films (corona treatment) | ○ |
| PP films (untreated) | × (peel off) |
| Epoxy resin | ○ |
| Urethane resin | ○ |
| Fe | ○ |
| Al | △ (partially peel off) |
| Glass | ○ |
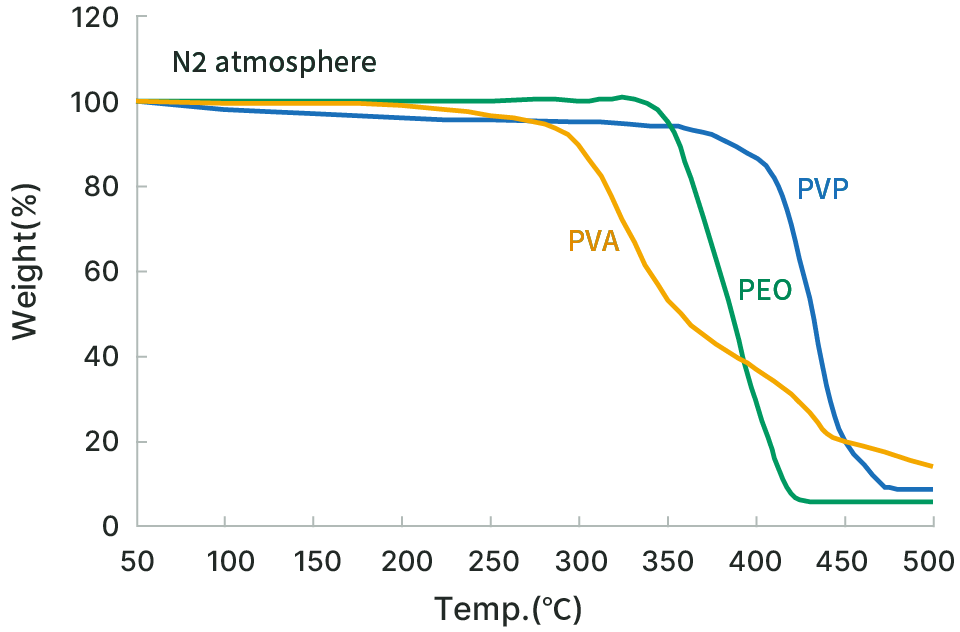
Excellent heat resistance
This product has superior heat resistance compared to other nonionic, water-soluble polymers.
Thermal decomposition behavior (Device: Rigaku Corporation’s THERMOFLEX TG8110)
Excellent hydrophilicity
This product can make a resin’s surface hydrophilic when it is kneaded with the resin.
Examples of PET
| None | PVP 5% added | |
|---|---|---|
| Contact angle | 81° | 67° |
| Water droplets on the surface |  |  |
| ΔL value before and after CB contamination | -32 | -9 |
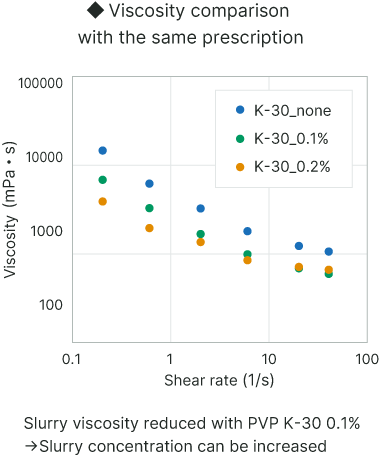
Excellent dispersion
This product can easily disperse CB and CNT.
◆ Examples of CB
No dispersant/PVP K-30 added
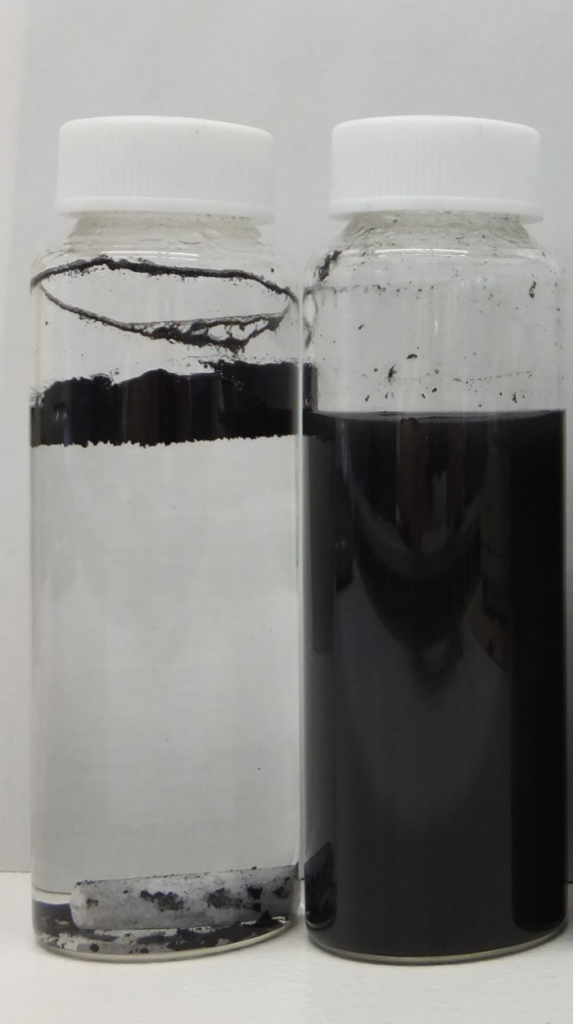

Dispersed CB in water, and left for one week
◆ Examples of CNT
No dispersant/PVP K-30 added
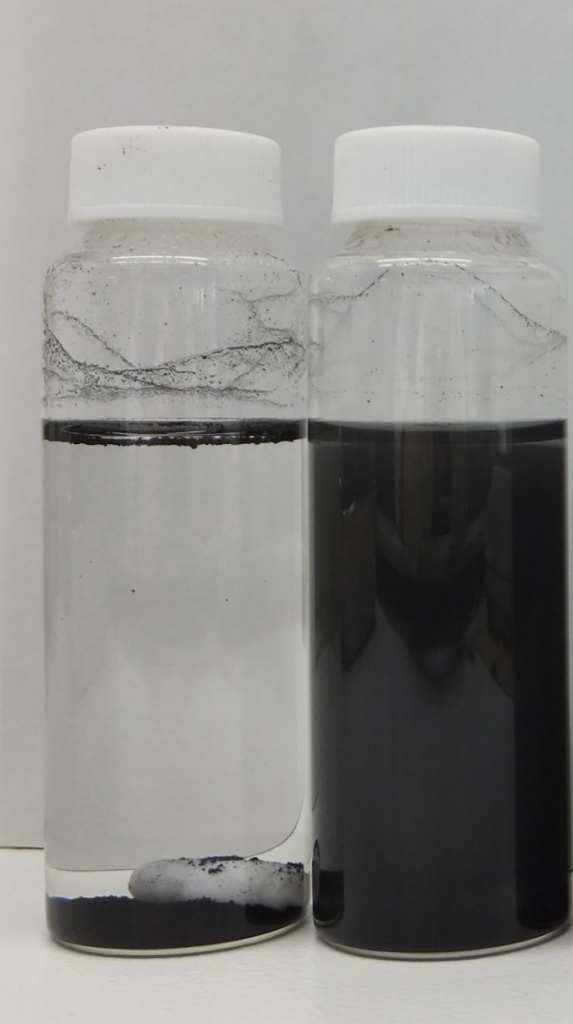

Dispersed CNT in water, and left for one day
This product can easily disperse carbon materials,in slurry for electrode.
| Good solvent | Poor solvent |
|---|---|
| Water | Benzene |
| Methanol | Toluene |
| Ethanol | Xylene |
| Isopropanol | Hexane |
| Butanol | Cyclohexane |
| Cyclohexanol | Mineral oil |
| Ethylene glycol | Diethyl ether |
| Propylene glycol | Tetrahydrofuran |
| Propylene glycol monomethyl ether | Dioxane |
| 1,4-Butanediol | Acetone |
| Glycerin | Methyl ethyl ketone |
| Diethylene glycol | Cyclohexanone |
| Glycol ether | Ethyl acetate |
| γ-butyrolactone | Carbon tetrachloride |
| Chloroform | |
| 2-Pyrrolidone | |
| N-Methylpyrrolidone | |
| N-Vinylpyrrolidone | |
| Acetic acid | |
| Butyric acid | |
| Pyridine | |
| Triethanolamine | |
| N,N-dimethylacetamide |
No insolubles = good solvent, insolubles = poor solvent
FAQ
- What is the metal content?
- Please refer to the data listed below as reference values.
K-85: 10 ppm max. (Pb conversion, coloring from acidic sodium sulfide test solution)
K-30: 5 ppm max. (ICP-MS) - How large is the particle size?
- The average particle diameter is as follows.
K-90, K-85: Approx. 300 μm
K-30: Approx. 100 μm - How should it be stored?
- This is a moisture-absorbing product so we recommend storing it in an air-tight container.(e.g.: Aluminum inner bag, with a heat-sealed)