Comprehensive Guide to Anti-blocking Agents
What is Blocking?
It is a phenomenon where films stick to each other during film production.
Since films are manufactured and stored in rolls, if films stick together, issues such as wrinkles during processing and the inability to peel off the film from the roll occur.
To ensure stable film production, anti-blocking measures for films are required.
What are Anti-blocking Agents?
Anti-blocking agents prevent blocking by forming protrusions to the film surface, thereby reducing the contact areas between films.
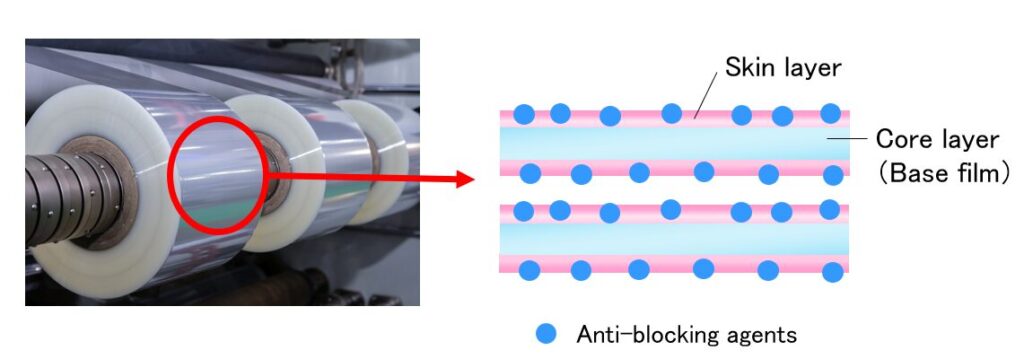
Generally, inorganic particles such as silica and organic particles such as acrylic particles are used.

Applications of Anti-blocking Agents.
Anti-blocking agents are used in a variety of films, including optical films and packaging films.

Characteristics Required in Anti-blocking Agents
(1) Add Slipperiness to the Film
Stable formation of protrusions on the film surface improves the film’s slipperiness.
(2) Less Drop off from the Film
If anti-blocking agents drop off during film production or processing, film performance will be reduced, and contamination due to dropped anti-blocking agents will occur.
In order to reduce drop off, an appropriate selection of anti-blocking agent particle size is effective.
(3) Maintain Transparency of the Film
Appropriate selection of anti-blocking agents can control film haze and transmittance.
While an increased quantity of anti-blocking agents causes haze to rise, selecting an anti-blocking agent with the same level of refractive index as the base film will prevent the haze from rising.
(4)Heat Resistance
It must be heat resistant and capable of withstanding the heating conditions during film molding.
Selecting an Anti-blocking Agent
Case1: Composition of Anti-blocking Agents
Anti-blocking agents are mainly divided into inorganic and organic particles.
Inorganic or organic particles are selected depending on the film composition and production method.
Case2: Film Production Methods
If the film production method is kneading, select powder; if it is coating, water-dispersed anti-blocking agents are to be selected.
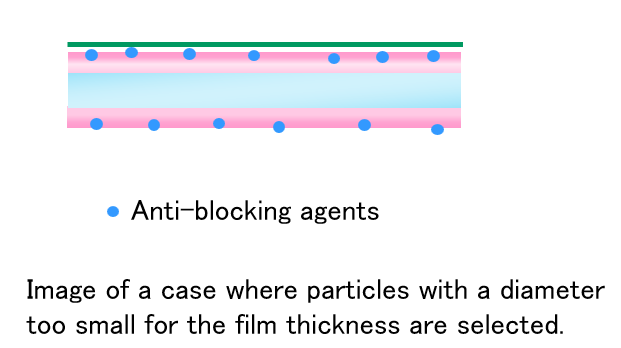
Case3: Particle Size & Particle Size Distribution
Evaluating multiple particle sizes and different particle size distributions will assist in selecting the optimum anti-blocking agent.
Case4: Refractive Index
To suppress the increase in film haze, select an anti-blocking agent with a refractive index similar to the film base resin.